Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose (HPMC) and Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (MHEC) are two of the most commonly used cellulose ethers derived from natural cellulose, a polymer found in the cell walls of plants. These compounds are modified through chemical processes to produce materials that exhibit thickening, water retention, film formation, and binding properties. While they share similar functional characteristics, they differ in chemical structure, properties, applications, and performance under various conditions.

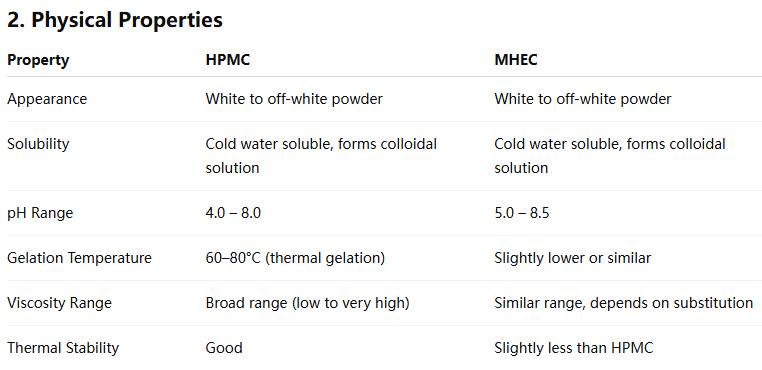
1. Chemical Composition and Structure
HPMC (Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose)
HPMC is a non-ionic cellulose ether produced by reacting cellulose with methyl chloride and propylene oxide. The hydroxyl groups (-OH) on the cellulose backbone are partially replaced by methoxy (-OCH₃) and hydroxypropyl (-CH₂CHOHCH₃) groups.
MHEC (Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose)
MHEC, on the other hand, is synthesized by reacting cellulose with ethylene oxide and methyl chloride. This introduces methoxy (-OCH₃) and hydroxyethyl (-CH₂CH₂OH) groups.
Key Differences in Structure:
HPMC has hydroxypropyl substituents, while MHEC contains hydroxyethyl groups.
The type of ether group affects the hydrophilicity, solubility, and thermal gelation behavior.
Viscosity Behavior: Both HPMC and MHEC are available in various viscosity grades, tailored for different applications. However, the molecular structure affects how viscosity behaves in solution. HPMC typically offers better thermal gelation and consistent viscosity over a wide pH range.
3. Functional Properties
Water Retention:
Both materials are excellent water retention agents, which is crucial in cement-based and gypsum-based systems. However, HPMC generally provides slightly better water retention, making it a preferred choice in dry mix mortars, tile adhesives, and renders.
Thickening Effect:
MHEC tends to yield a smoother and more stable viscosity in aqueous solutions, making it desirable for applications where consistent flow and workability are needed.
Film Formation:
HPMC tends to form more flexible and transparent films, while MHEC forms softer films. These differences impact applications in surface coatings and adhesives.
Thermal Gelation:
HPMC undergoes thermal gelation, forming a gel upon heating. MHEC also exhibits thermal gelation, but to a lesser degree. This property is particularly important in pharmaceutical and food applications where a gel barrier or texture is desired.

4. Applications
Both HPMC and MHEC are used in a broad range of industries. However, certain performance characteristics make one more suitable than the other for specific applications.
4.1Construction Industry
HPMC:
Tile adhesives
Cement-based plasters and renders
Self-leveling compounds
External insulation finishing systems (EIFS)
Gypsum-based plasters
Advantages in Construction:
High water retention
Better open time in adhesives
Improved workability
MHEC:
Skim coats
Lightweight plaster
Wallpaper adhesives
Ready-mixed joint compounds
Advantages in Construction:
Smooth consistency
Good adhesion properties
Easy mixing behavior
4.2Pharmaceuticals
HPMC:
Used as a binder and film-coating agent in tablets
Controlled drug release matrix systems
Eye drops and ophthalmic gels
MHEC:
Less commonly used due to its lower gelation properties, but still applicable in:
Oral suspensions
Topical formulations
4.3Paints and Coatings
MHEC:
Often preferred in water-based paints due to superior pseudoplastic behavior (shear-thinning)
Enhances brushability and smooth application
HPMC:
Also used in paints, particularly when higher water retention or gelation properties are required
D. Detergents and Personal Care
HPMC:
Shampoos, conditioners, and lotions
Acts as a thickener and stabilizer
MHEC:
Hand soaps and body washes
Preferred for improved clarity and ease of formulation
4.4Food Industry
HPMC:
Approved as a food additive (E464)
Used in vegetarian capsules, bakery products, and emulsified sauces
Helps in texture and stability
MHEC:
Not as widely approved for food use; limited application
5. Environmental and Regulatory Aspects
Both HPMC and MHEC are non-toxic, biodegradable, and non-ionic, making them safe for use in many products. However:
HPMC is more widely approved for pharmaceutical and food use.
MHEC is primarily used in industrial and cosmetic applications.
6. Cost and Availability
MHEC is generally more cost-effective than HPMC due to its slightly simpler production process and lower demand in pharmaceutical and food-grade markets. However, HPMC’s broader application scope, especially in regulated industries, justifies its higher price.
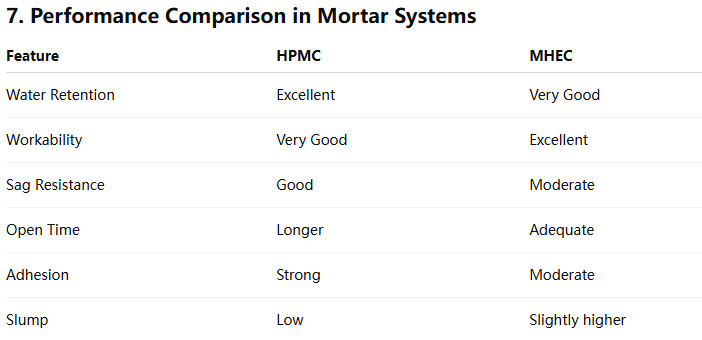
In high-performance systems like tile adhesives or renders where high water retention and adhesion are needed, HPMC is preferred. In contrast, for smooth application and ease of mixing, such as in joint compounds or wall putties, MHEC can be more efficient.
While HPMC and MHEC are chemically similar cellulose ethers, their distinct substituent groups (hydroxypropyl in HPMC vs. hydroxyethyl in MHEC) lead to meaningful differences in performance, especially in terms of thermal gelation, water retention, film formation, and application compatibility.
Post time: May-14-2025